Defenders of globalization are on solid ground when they criticize President Trump’s threats of punitive tariffs and border walls. The economy can’t flourish without trade and immigrants.
But many of those defenders have their own dubious explanation for the economic disruption that helped to fuel the rise of Mr. Trump.
At a recent global forum in Dubai, Christine Lagarde, head of the International Monetary Fund, said some of the economic pain ascribed to globalization was instead due to the rise of robots taking jobs. In his farewell address in January, President Barack Obama warned that “the next wave of economic dislocations won’t come from overseas. It will come from the relentless pace of automation that makes a lot of good middle-class jobs obsolete.”
Blaming robots, though, while not as dangerous as protectionism and xenophobia, is also a distraction from real problems and real solutions.
The rise of modern robots is the latest chapter in a centuries-old story of technology replacing people. Automation is the hero of the story in good times and the villain in bad. Since today’s middle class is in the midst of a prolonged period of wage stagnation, it is especially vulnerable to blame-the-robot rhetoric.
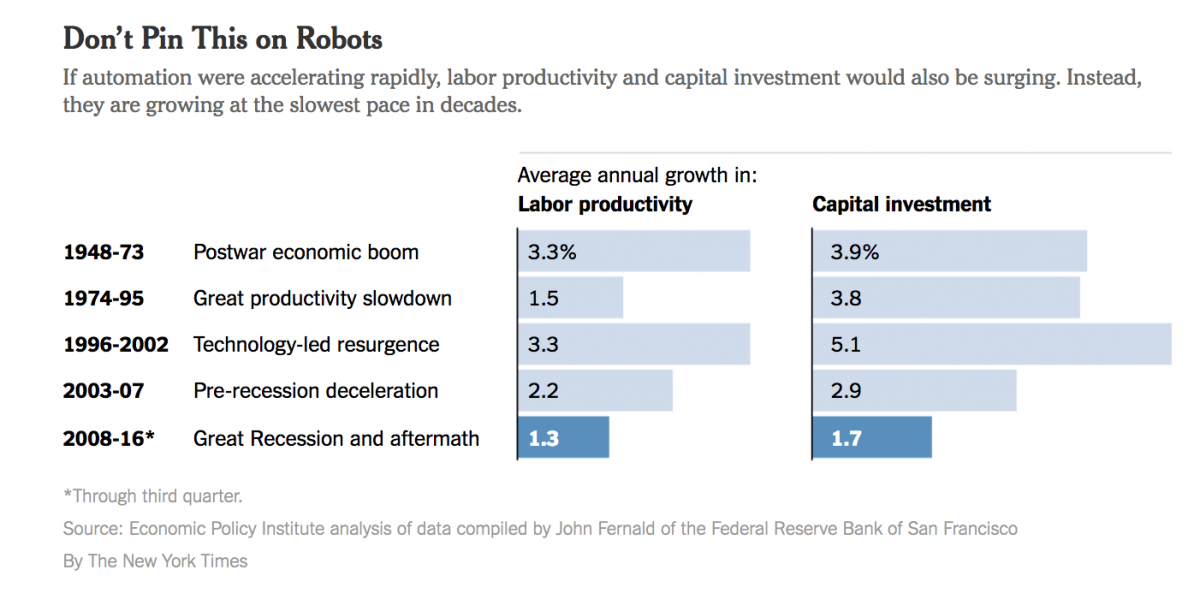
And yet, the data indicate that today’s fear of robots is outpacing the actual advance of robots. If automation were rapidly accelerating, labor productivity and capital investment would also be surging as fewer workers and more technology did the work. But labor productivity and capital investment have actually decelerated in the 2000s.
While breakthroughs could come at any time, the problem with automation isn’t robots; it’s politicians, who have failed for decades to support policies that let workers share the wealth from technology-led growth.
The response in previous eras was quite different.
When automation on the farm resulted in the mass migration of Americans from rural to urban areas in the early decades of the 20th century, agricultural states led the way in instituting universal public high school education to prepare for the future. At the dawn of the modern technological age at the end of World War II, the G.I. Bill turned a generation of veterans into college graduates.
When productivity led to vast profits in America’s auto industry, unions ensured that pay rose accordingly.
Corporate efforts to keep profits high by keeping pay low were countered by a robust federal minimum wage and time-and-a-half for overtime.
Fair taxation of corporations and the wealthy ensured the public a fair share of profits from companies enriched by government investments in science and technology.
Productivity and pay rose in tandem for decades after World War II, until labor and wage protections began to be eroded. Public education has been given short shrift, unions have been weakened, tax overhauls have benefited the rich and basic labor standards have not been updated.
As a result, gains from improving technology have been concentrated at the top, damaging the middle class, while politicians blame immigrants and robots for the misery that is due to their own failures. Eroded policies need to be revived, and new ones enacted.
A curb on stock buybacks would help to ensure that executives could not enrich themselves as wages lagged.
Tax reform that increases revenue from corporations and the wealthy could help pay for retraining and education to protect and prepare the work force for foreseeable technological advancements.
Legislation to foster child care, elder care and fair scheduling would help employees keep up with changes in the economy, rather than losing ground.
Economic history shows that automation not only substitutes for human labor, it complements it. The disappearance of some jobs and industries gives rise to others. Nontechnology industries, from restaurants to personal fitness, benefit from the consumer demand that results from rising incomes in a growing economy. But only robust public policy can ensure that the benefits of growth are broadly shared.
If reforms are not enacted — as is likely with President Trump and congressional Republicans in charge — Americans should blame policy makers, not robots.
3 WAYS TO SHOW YOUR SUPPORT
- Log in to post comments